Understanding the Role of Hormones in Weight Gain
Being overweight doesn’t just happen when you eat too much or move too little. Other significant factors contribute to gaining weight, including hormones.
Hormones are chemical substances responsible for traveling throughout the body and helping cells and organs function. In simple words, they’re referred to as “messenger molecules.”
About Hormones
Hormones are the body’s chemical messengers. They help the body maintain homeostasis (tendency of an organism to maintain a stable internal state), regulate our metabolism, and support our sexual function.
The endocrine system regulates hormone production and includes the hypothalamus, pineal gland, and pituitary gland in the brain, as well as other organs in the rest of the body such as the adrenal glands, thyroid, pancreas, and gonads (male and female reproductive glands).
As we age, our bodies naturally produce fewer hormones. This can lead to a decline in physical and mental health. When the body can no longer regulate hormone function optimally, imbalances can occur. Unfortunately, an imbalance of hormones in the body can cause dozens of detrimental conditions, including the following:
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Hormonal Acne
- Thyroid Disease
- Infertility
- Irregular Menstrual Cycle

Hormone Changes Throughout the Lifetime
Hormones that affect our weight can fluctuate depending on our sex, weight, medical conditions, and age. During adolescence, the body goes through many changes. An increase in the male and female sex hormones, estrogen and testosterone, causes enduring changes.
Similarly, life events such as pregnancy and illness can cause our hormones to fall out of balance later in life. In particular, men and women experience marked decreases in sex hormone production with age.
Signs of Hormonal Imbalance in Adults
Alongside increased weight, other signs of hormonal imbalance in adults include the following:
- Increased or decreased heart rate
- Gastrointestinal disruption (diarrhea or constipation)
- Mood disorders (depression, anxiety)
- Poor skin, hair, and nail condition
- Fatigue and disrupted sleep
- Decreased tolerance to temperature change
- Higher than normal cholesterol
Hormones That Affect Weight
There are many factors that contribute to a person’s weight. Some are related to lifestyle. Others are unseen and related to our individual biology. Hormones that regulate how much body fat we store are one of those unknown factors.
Below are the hormones that influence a person’s weight:
Leptin
Leptin is produced in body fat. It’s a hormone that tells our brain how much body fat we have and helps keep our weight steady in a normal range. When we gain weight, our leptin level goes up. This reduces our appetite and promotes energy expenditure to cause weight loss, bringing us to our previous weight. If we lose weight, our leptin level goes down and, likewise, we eat more food and our metabolism slows.
A common problem in obesity is “leptin resistance,” where the leptin level is high but it is not causing weight loss as it should. When this happens, you maintain the newer higher weight, rather than return to your previous lower weight.
Ghrelin
Ghrelin plays a key role in our appetite and food intake regulation. It is essentially the opposite of leptin. It’s the “hunger hormone” that sends a message to your hypothalamus (area of the brain), indicating that your stomach is empty and needs food. Its main function is to create appetite.
When we skip a meal, our ghrelin level becomes very high, so we eat more food at the next meal and can sometimes overeat. What we eat also affects ghrelin. Carbohydrate is the most effective macronutrient to lower your ghrelin level. Protein is less effective but works to keep ghrelin suppressed for longer.
Normally, ghrelin levels are highest before eating and lower after a meal. Curiously, research indicates that people with obesity have low ghrelin levels but are more sensitive to its effects. This sensitivity may lead to overeating.

Cortisol
Cortisol is known as the stress hormone and is produced by your adrenal glands.
During times of stress, the hormone triggers an increase in heart rate and energy levels. The release of cortisol alongside the hormone adrenaline is commonly called the “fight or flight response.”
While it’s important for your body to release cortisol in dangerous situations, chronic high levels may lead to health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, low energy levels, high blood pressure, sleep disturbances, and weight gain.
Certain lifestyle factors—including poor sleep habits, chronic stress, and a high intake of high-glycemic food—may contribute to higher cortisol levels.
Not only does obesity raise cortisol levels, but high levels may cause weight gain, creating a negative feedback loop.
Estrogen
Estrogen is a female sex hormone that influences a person’s weight whether high or low. Levels of this hormone change during life stages such as pregnancy, nursing, and menopause, as well as throughout the menstrual cycle.
High levels of estrogen, which are often seen in people with obesity, are associated with an increased risk of certain cancers and other chronic diseases.
Conversely, low levels—typically seen with aging, perimenopause, and menopause—may affect body weight and body fat, therefore also increasing your risk of chronic ailments.
Individuals with low estrogen levels often experience central obesity, which is an accumulation of weight around the trunk of the body. This can lead to other health problems such as high blood sugar, high blood pressure, and heart disease.
You can lower your risk of many of these health conditions through lifestyle changes, especially by maintaining a healthy body weight.

Insulin
Insulin, the main storage hormone in your body, is produced by your pancreas. In healthy individuals, insulin promotes the storage of glucose—a simple sugar you get from your food—in the muscle, liver, and fat cells.
Insulin resistance is a fairly common condition that causes your cells to stop responding to insulin. The condition results in higher blood sugar because the insulin cannot move glucose into your cells. Your pancreas then produces even more insulin in an attempt to boost glucose absorption.
Insulin resistance has been linked to obesity, which in turn can play a role in other conditions, such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Thyroid Hormones
The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism. Certain thyroid conditions can impair the thyroid’s production of these hormones, which can lead to weight gain or weight loss.
Treatment of an overactive thyroid generally causes weight gain. However, treatment of an underactive thyroid has not been shown to cause weight loss. So, although the thyroid hormone has an important role in our metabolism, it does not seem to be helpful for weight loss.
How Diet and Lifestyle Can Affect Hormones
Lifestyle factors can have a significant impact on hormone levels. While genetic and underlying medical conditions can influence hormone levels to some extent, lifestyle choices also play a substantial role in maintaining hormonal balance.

Diet
Nutrition is a critical factor in hormone production and regulation. A balanced diet with adequate nutrients, including essential fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals, supports the synthesis of hormones.
Physical Activity
Regular exercise has been shown to have a positive impact on hormone levels, improve sensitivity to hormones, and balance sex hormones. However, excessive exercise or overtraining can lead to imbalances, particularly in female sex hormones.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can significantly affect hormone levels, particularly cortisol, the primary stress hormone. Prolonged elevation of cortisol can disrupt the balance of other hormones, impacting reproductive hormones, thyroid hormones, and insulin. Practices such as mindfulness, meditation, and adequate sleep can help manage stress and promote hormonal balance.
Sleep
Quality and duration of sleep play a vital role in hormone regulation. Insufficient or disrupted sleep can affect the release of cortisol, insulin, and leptin. Establishing good sleep habits is essential for maintaining hormonal balance.

Body Weight and Composition
Body fat levels can influence hormonal balance, particularly sex hormones. Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, can lead to increased estrogen production in both men and women. Maintaining a healthy body weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise contributes to hormonal health.
Alcohol and Substance Use
Excessive alcohol consumption and the use of certain substances (cigarettes, drug use) can impact hormone levels. Alcohol, for example, can affect the liver’s ability to metabolize hormones, leading to imbalances. Substance abuse can disrupt the endocrine system, affecting various hormones.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to environmental toxins, such as endocrine-disrupting chemicals found in certain plastics, pesticides, and pollutants, can interfere with hormonal production and function. Minimizing exposure to these substances can contribute to hormonal balance.
Age and Life Stage
Hormone levels naturally fluctuate with age and life stages. Puberty, pregnancy, menopause, and aging all bring about hormonal changes. While these changes are a normal part of life, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help manage hormonal fluctuations associated with these transitions.
How Semaglutide Can Help With Obesity
Other than maintaining a proper diet, exercising, and reducing stress, there is another way to help battle obesity caused by hormones: taking semaglutide. Semaglutide works as a weight-loss drug that assists the pancreas in releasing the right amount of insulin.
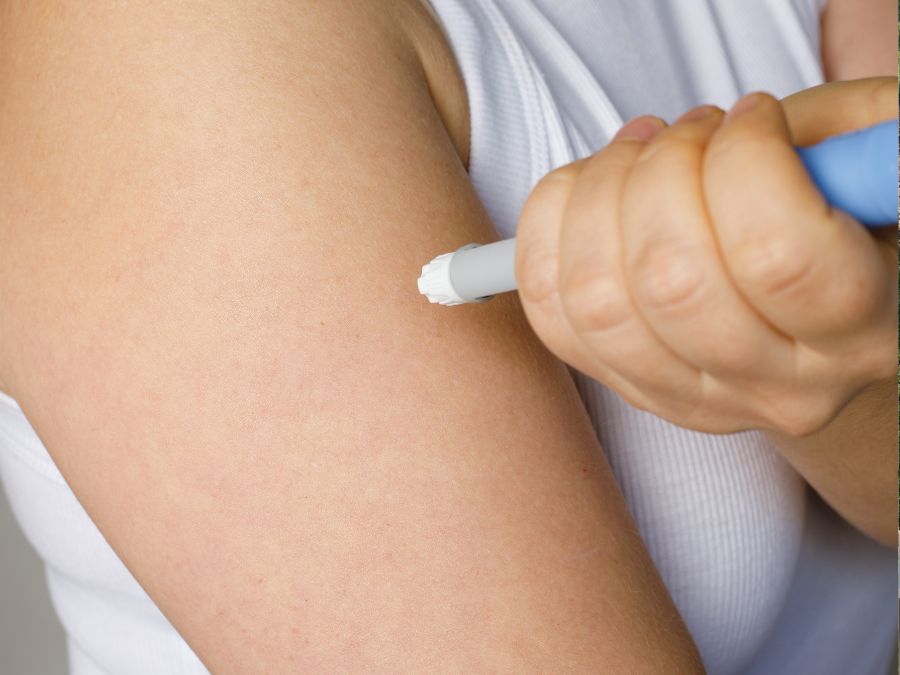
What Is Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is a type of medication known as GLP-1 receptor agonists, which leverage the body’s natural systems to improve glycemic control and aid in weight reduction. Its development was guided by the understanding of the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) hormone, which influences insulin secretion and promotes satiety.
The unique aspect of semaglutide lies in its long-acting nature, allowing for less frequent dosing compared to other medications in the same class. This improves patient adherence and overall treatment efficacy.
Approved in rigorous clinical trials, semaglutide has been recognized for its dual benefits: managing blood sugar levels in adults with type 2 diabetes and facilitating weight loss in individuals with or without diabetes when combined with diet and exercise.
Benefits of Semaglutide for Weight Loss Management
- Significant Weight Reduction – Clinical trials have demonstrated that semaglutide can lead to substantial weight loss in individuals who are overweight, particularly when combined with lifestyle modifications
- Improved Metabolic Health – Semaglutide improves markers of metabolic health, including reductions in waist circumference, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels
- Lower Risk of Weight-Related Health Issues – The weight loss achieved with semaglutide can reduce the risk of developing weight-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke
- Sustainable Weight Management – It supports long-term strategies by encouraging healthier eating habits and improving the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels
- Flexibility in Treatment Plans – Semaglutide can be used alongside other weight management strategies, offering a versatile option for individuals tailoring their approach to weight loss
Who Is a Good Candidate for Semaglutide Injections?
Semaglutide injections are best suited for individuals seeking a medically supervised approach to weight management. Ideal candidates often have a body mass index (BMI) that falls within the criteria for being obese or overweight and may also have weight-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol.
These injections are especially beneficial for those looking for a treatment option that can be seamlessly integrated into a comprehensive health and wellness plan.
To determine if you are a good candidate for semaglutide injections, it’s important to have a personalized consultation with a healthcare professional. At Live Oak Weight Loss, we assess your medical history, current health status, and weight management goals to tailor our treatment plan to your unique needs.

Semaglutide and Lifestyle Changes: Maximizing Your Benefits
While semaglutide is a powerful tool for weight loss, it’s most effective when combined with a healthy lifestyle. The medication creates an environment in your body that’s conducive to weight loss, but it’s up to you to capitalize on these effects through diet and exercise.
For instance, the appetite-suppressing effects of semaglutide can make it easier to stick to a balanced, nutritious diet. Similarly, its potential to increase energy expenditure can be amplified by regular physical activity. By combining the medication with lifestyle changes, you can achieve significant and sustainable results.
Are you ready to experience the transformative effects of semaglutide yourself? Contact Live Oak today at (843) 386-5331 for a personal consultation and let semaglutide help you unlock your body’s full potential.





